Welcome to the website about projectile motion. This is the basis of ballistics - a very interesting part of mechanics.


Projectile motion is motion performed by an object in uniform gravitational field, where gravity is the only force affecting this motion.
As we are not engineers launching precius rockets, we can simplyfy projectile motion for our idealised model
1. Air resistance is negligible and will not be taken into account
2. Gravitational acceleration is constant regardless of distance from the ground
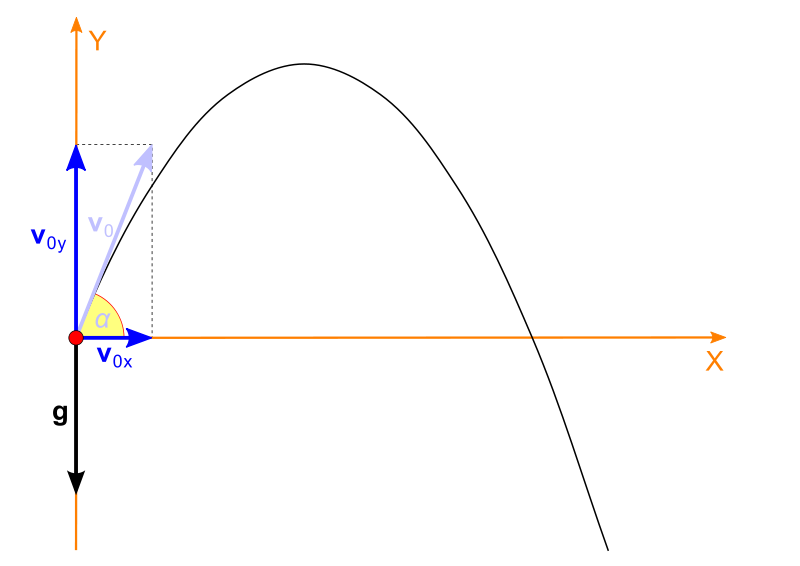
3. We launch our projectile at angle theta and velocity v0 from the origin
Galileo has shown that the curved path that projectile follows is parabola. The only special case is when projectile is launched perpendicularily to the ground - then the path is a straight vertical line.
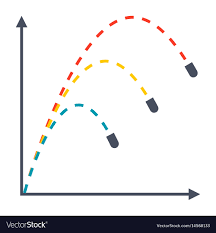
In projectile motion, the horizontal motion and the vertical motion are independent of each other and we should think about them individually. This is the principle of compound motion established by Galileo in 1638, and used by him to prove the parabolic form of projectile motion.
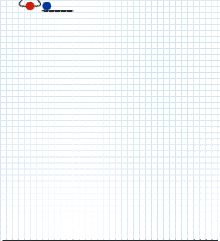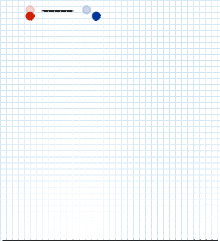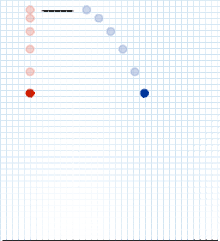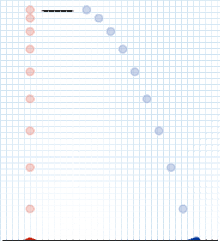
Now, when we know that we will consider this motion as compound of vertical and horizontal one, we can write down the two initial velocities:
As there is no external force acting on the body other than vertical gravitational force:
As there is no horizontal acceleration, horizontal velocity stays the same throughout the motion, while vertical velocity changes similarily to velocity of free fall (derived from kinematic equations):
We can also determine magnitude of velocity, using Pythagorean theorem:
Plugging in previous data to kinematic equations, we get:
The magnitude of displacement is:
Total time of flight is equal to:
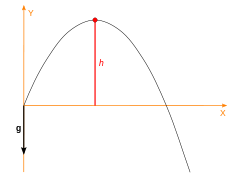
Maximum height is achieved in vertex of parabola. As height of launch is 0 and parabola is symmetrical , maximum height will be halfway and time to achieve maximum height will be half of the time of flight.
Then:
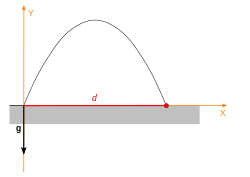
Note, that in order to maximise the distance sine of 2 theta should be equal to 1, therefore
theta should be equal to 45 degrees. This is the angle, from which projectile will travel the farthest
In this case: